The
liver is an organ attached to the digestive system from the wedge shape, shaped by its relationship with adjacent organs and muscles. It is covered by a connective capsule, known as Glisson's capsule, which protects it but does not contribute significantly to its shape. It weighs about 2 kg , equivalent to 2.5% of body weight of an adult man of medium build, in the infant liver weights for the largest development in relation to the rest of the body can get to be 5% of total. The liver tends to reach its largest size at 18 years of age, after which its weight decreases gradually with increasing age. The liver surface is smooth and soft, reddish-brown, but in obese subjects may appear yellow, due to widespread infiltration of adipose tissue in the liver parenchyma (steatosis).
ReportsThe liver is located in the upper abdominal cavity, it occupies almost all in right hypochondria and epigastrium, going with the left lobe to occupy a part of hypochondria left, which may be more or less visible depending on the subject . Its upper surface is at the level of the 5th coast and the 10th thoracic vertebra, while the infero-lateral summit pushes up costs at the 11th and the 2nd lumbar vertebra. Above Glisson's capsule and the peritoneum (except for a small triangular area) separate it from the diaphragm, anterior-lateral and relationship with the diaphragm that separates it from the right pleura, sometimes the left lobe is related in the same way with the left pleura inferiorly by the transverse colon, the antrum of the stomach, kidney and adrenal gland, right, rear with the gallbladder, fundus of the stomach, esophagus and the inferior vena cava.
LobiThe liver, according to the classical distinction and is divided into four lobes: right, left, square, and caudate.
The right lobe is the most voluminous organ, vaguely shaped dome that covers at least part of all the five faces of the liver. Conventionally, the falciform ligament superiorly and inferiorly venous ligament separating it from the left lobe, but now this distinction is no longer accepted.
The left lobe has a volume equal to about half of the right and is thinner, has a triangular shape.
The lobe is square on the back surface of the liver, and appears as a rectangular projection, is functionally related to the left lobe. Its boundaries are the right fossa cyst and the gallbladder, the hepatic hilum superiorly, laterally round ligament.
The caudate lobe is a projection of the rear surface of the liver, consisting of the papillary process and the caudate process, is also functionally related to the left lobe. It is bordered inferiorly by the ILO hepatic venous lateral ligament superiorly and medially from the hepatic veins from the inferior vena cava.
FacesThe surface of the liver is commonly divided into five faces: top, front, right, back and bottom. The top sides, front and right side are continuous with each other and we can refer to all calling diaphragmatic surface of the liver.
The upper face, in the area between the upper margin of 5 ° and the lower coast of the 6th, is the largest, has a pear shape and is separated from the dome of the right diaphragmatic peritoneum, an exception ' triangular area in which the two layers of the falciform ligament diverge, leading to direct contact between the diaphragm and the Board. The center and level the divergence of the falciform ligament there is a slight depression, that impression rate. Is the anterior superior surface of right and left lobes.
The front face is convex and has a triangular shape, is at the lower edge of the area between 6 th ee coast of the upper 10 °. It is also covered by peritoneum except for the insertion of the falciform ligament. Part of this is related to the diaphragm, which covers the front. Sometimes mild depression can be distinguished elongated, finger ribs. Forms the anteroinferior surface of the right lobe and left lobe.
The right side is convex and in accordance with the right diaphragmatic dome, which shapes the form and separates it from the right lung. The diaphragm covers the front by the sixth to the ninth or tenth coast. Includes the right side surface of the right lobe.
The back is broad, convex to the right but with a concavity determined by the convexity of the spine. Includes the rear surface of the right lobe of the liver and the caudate lobe. It is joined to the diaphragm by connective tissue and is a large triangular area naked. Hepatic hilum side has a vertical hole which is housed in the inferior vena cava. And below the bare, there is a small triangular depression, the imprint of the adrenal side and below it a deep concavity which is oval rather instead the imprint failure, determined by the right kidney. Footprint kidney medially there is another slight concave oval, the duodenal impression, determined by the first portion of the duodenum. Below this there is a footprint renal semicircular depression, the colic impression, determined by the hepatic flexure.
The underside includes a rear surface of most of the left lobe and the lower half of the right lobe and the hilum and the liver lobe square. In a shallow grave postero-medial to the inferior vena cava, houses the gallbladder. On the left lobe are the footprint and the footprint of gastric esophageal (determined by abdominal section of the esophagus), two adjacent depressions. The imprint colic may sometimes be on this side.
LigamentsThe liver has several peritoneal ligaments that connect to other organs, the anterior abdominal wall and diaphragm, falciform ligament, coronary ligament, round ligament, left triangular ligament, Right triangular ligament, venous ligament, lesser omentum (hepato-gastric ligament).
The falciform ligament is formed from two sheets placed on the front and top sides of the liver and is classically considered to be the divisor of its right and left lobes. Above the two layers differ and are the coronary ligament. The round ligament, which is a remnant of the left umbilical vein, is less than the continuation of the falciform ligament and protrudes from the liver into the abdominal cavity, dividend, on the back surface of the organ, the left lobe by lobe square.
The coronary ligament is continued on the back surface of the leaflets of the falciform ligament. In the left lobe of the coronary ligament merges with the package left venous ligament, giving rise to the left triangular ligament, in the right lobe merges with the right package of venous ligament, giving rise to the right triangular ligament. Here also defines the bare triangular area of the liver in direct contact with the diaphragm, as well as a smaller one at the left lobe.
The left triangular ligament is composed of a double layer of peritoneum that is continuous with the falciform ligament before and after the lesser omentum. The right triangular ligament is rather a continuation of the coronary ligament.
The ligament is the residual venous anastomosis vein present during fetal life between the portal vein and the left hepatic vein. Begins in the wake of venous ligament, located on the rear surface of the liver, as opposed to the falciform ligament. Divides the left lobe of the liver from the caudate lobe.
The lesser omentum or hepato-gastric ligament is a peritoneal fold that connects the back surface of the liver to the small curvature of the stomach (pars flaccida) and the first portion of duodenum (pars TENS). The Pars Tensa contains within it the formations hepatic pedicle . The hepato-duodenal ligament is to define the hole epiploico Winslow. Has a shape that is defined as "L", where the vertical line indicates the venous ligament and the horizontal to the continuation of the lesser omentum at the hilus. It continues in the right coronary ligament and left triangular ligament.
SectorsThe liver, however, is no longer divided, as it was following the procedures macroscopic anatomical surface, in right and left lobes by the falciform ligament, but will instead be studied on the basis of vascular, as proposed by Claude Couinaud in 1957., because they are more closely related to the physiology of the organ. A distinction is therefore four sectors (right lateral, right medial, left medial, left lateral), each determined by a branch of the portal vein, and six slots (right portal, the main portal, umbilical, left portal, venous, Gans), or cross-cutting areas. Each sector is further divided into 1-4 segments, for a total of nine segments, which are conventionally referred to by the corresponding Roman numeral. The segments are divided based on the tertiary branches of the portal vein, hepatic artery and bile ducts that are contained in the stalks glissoniani because enveloped by the sheath of Glisson. Starting from the right lobe of the liver to the left and whereas the front surface of the liver can be distinguished:
The right lateral sector, formed from segment VII superiorly and inferiorly by the VI
The media sector right format at the top and bottom of the eighth segment V.
The left medial area, formed from the side of I and IX segment, medial to them by the III and IV (medial to IV).
The left lateral field, formed from the second segment.
CracksThe slots are divided into major (left main, left), which contain the hepatic veins and minor (umbilical vein, Gans), which does not contain them.
The main portal fissure is between the apex of the gall bladder and the imaginary vertical line passing through the center of the inferior vena cava. Divides the right lobe of the left lobe, the medial area from the right medial left field. Welcomes the hepatic vein media.
The left portal fissure divides the left lobe of the liver in the left lateral and medial left in the field. Welcomes the left hepatic vein and extends from the falciform ligament and left triangular ligament.
The right portal fissure divides the right lobe of the liver in the right medial and right lateral fields. Granting the right hepatic vein.
The umbilical fissure separates segment II from segment III in the left lobe of the liver and contains the umbilical vein in the slot, one of the two major branches of the left hepatic vein, and some branches of the hepatic left. Corresponds to the insertion of the falciform ligament.
The fissure vein is the continuation of the umbilical fissure on the lower surface of the liver and corresponds to the groove of venous ligament, then runs between the caudate lobe and segment IV.
The slot is located behind the Gans cystic fossa, below the right lobe.
SegmentsHere are the nine segments of the liver where it is now divided.
The segment corresponds to the caudate lobe, is represented only in the posterior surface of the liver. It is located posterior to segment IV. Side there is the seventh segment, distinct from the inferior vena cava which runs in its groove, the medial segment II, which is divided by the groove of the venous ligament. Receives branches from the middle hepatic vein, left and right hepatic artery, drains into the inferior vena cava.
The segment II is the only range in the left side, so is the side of the whole liver. Medially and inferiorly to it is the third segment, and is divided by the segment from the falciform ligament. Drains into the left hepatic vein, and in rare cases, directly into the inferior vena cava.
The third segment is the side of the left medial area, therefore the gap between the umbilical and left portal fissure. Side to it is the fourth segment, the medial segment II. Drains into the left hepatic vein.
The fourth segment is the lateral portion of the left medial sector, is between the main portal fissure and the umbilical slit. Medially it is the third segment, lateral segment of the V (the edge of this segment passes through the vertical axis of the gall bladder) and part of the segment, with the upper segment IX. Hepatic vein drains mainly in the media, but has smaller branches in the left hepatic vein.
The fifth segment is the lower portion of the medial right sector of the liver. It is bordered medially with the fourth segment, the side with the sixth segment, with the upper segment VIII. You crack between right portal and main portal fissure. Drains into the right hepatic vein and hepatic vein in the media.
The sixth segment forms the lower portion of the right lateral sector. It is bordered medially by the V segment, with the upper segment VII and a small portion on the lower surface of the liver with the ninth segment.
The seventh segment forms the upper portion of the right lateral sector. It is bordered medially by the anterior segment VIII, while the latter is divided by the segment from the inferior vena cava inferior with the sixth segment. His veins draining into the right hepatic vein and may reach the inferior vena cava through the right middle hepatic vein.
Segment VIII is only present on the anterior surface of the liver, is the upper portion of the right medial area of the organ. It is bordered laterally with the segment VII, with the V segment inferiorly, medially with the fourth segment. Drains into the middle hepatic vein and right hepatic vein.
The ninth segment, represented only in the rear surface of the liver, is a subdivision of the segment and represents the right side, that is next to the inferior vena cava. The drains in the same vein segment. Lower boundary with the fourth segment VII laterally with the upper segment and the segments.
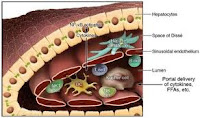
Ilo liverThe ILO is composed by a depression located on the lower surface of the liver, which is located posterior to the square lobe and anterior caudate lobe. Receive the neurovascular bundle directly to the liver and bile ducts made up primarily of two liver from the hepatic artery, the portal vein, some lymphatic vessels and nerves that make up the hepatic nerve plexus. Each beam structure is covered by the sheath of Glisson hepatobiliary, composed of loose connective tissue, the same one that covers the surface of the faces of the liver that accompanies each pot until the penetration in one or more liver segments. In the space between a vessel and the other is the loose connective tissue support. Just before entering the liver parenchyma, bile duct branches in the duct and right hepatic duct in the left hepatic duct, which then penetrate the hilum, these bile ducts are more anterior ducts of the hepatic hilum. Posteromedial to the two hepatic ducts, starting in the two branches of the hepatic artery (left hepatic artery and right hepatic artery), with the right hepatic artery of greater caliber than the left. Later the two branches of the hepatic portal vein enter the hilum with its two branches (the left portal vein and right portal vein), the right size larger than the left. All these vessels entering the hilum in supero-lateral direction. In the space between the two branches of the hepatic artery and portal vein starting in different lymphatic vessels of small caliber, more rarely, he found someone laterally, or medially before hepatic artery. Numerous nerves (nerves and nerves of the left lobar lobar right) shall run with both portal vein and hepatic artery between it and the two hepatic ducts.
ArteriesThe hepatic artery is the main artery that supplies the liver. Originates from the celiac trunk, common hepatic artery, where it is called, then the front door and side passes the rear of the hole epiploico, the duodenum and superiorly by the lesser omentum. During its course issues such as its branches left gastric arteries (thick) and the gastroduodenal artery and right. At this point is called the proper hepatic artery. Following the upper curve in front of and behind the portal vein, hepatic artery branching into left and right hepatic artery. The right hepatic artery has a sinuous course, goes back to the duct common bile duct, which then emits its ramifications now the cystic artery, which descends antero-inferiorly on the gallbladder, and upper back behind the right hepatic duct. At this point enters the liver parenchyma, horizontal folds and divides into two further branches, one proceeds antero-superiorly and supplying the segments I, V, VIII, each with a branch, the other runs laterally and posteriorly and supplies arterial branches to VI, VII segment. The left hepatic artery of lower caliber, upper back, and here enters the liver parenchyma is divided into three branches, one side for the fourth segment, a top for the third, one medial for the second. The segmental arteries are terminal type.
VeinsThe liver has two venous systems, that of the portal and hepatic veins.
The portal vein, which originates from the confluence of lienale vein and superior mesenteric vein, dates back to the hole before and after epiploico gastric artery and hepatic bile ducts. Prior to it starting in some lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes can be found, and some nerves making up the hepatic nerve plexus. Shortly before entering the liver parenchyma is divided into left and right portal vein, with the right size larger. The left branch has a course longer and more horizontal than the right, just entered the parenchyma becomes more horizontal and emits a small branch to the posterior segment I, the rest continues horizontally until fork in a branch that descends anterior-inferior and divides into two stems that are directed to the medial and lateral to the third to the fourth segment. The other branch continues horizontally entering in the second segment. The right portal vein, larger and shorter, now branching into two branches, an anterior-lateral folds and divides into two stems, the upper sprays the eighth segment, the lower V, the other branch continues postero-laterally to fork in a branch than for the seventh and the sixth in a lower segment.
The three hepatic veins (left, middle and right) tributaries of the inferior vena cava was identified as the venous system of the liver. Their course in the liver parenchyma allows you to split the liver in the fields, their peduncles allow to divide each sector into further segments. The right hepatic vein is the largest of three runs in the top right portal fissure, inferiorly draining segments V and VI each with a stalk, the upper segments VII and VIII, and then go and lead supero-medially in the inferior vena cava. The corresponding fields are the right lateral and medial side of right. The middle hepatic vein runs in the main slot, bottom drains segments V (medial) and IV (side), the upper part VIII (medial) and again the fourth, then come out in the inferior vena cava. The corresponding fields are the right medial and left medial. A small vein, branch of the inferior vena cava, drains the individual segments. The left hepatic vein drains inferiorly (umbilical vein) segments IV (medial) and III, while the second segment is drained, the other horizontal stems. Sometimes it may issue a stalk to the fourth segment. The corresponding fields are the left medial and left lateral.
LymphThe liver has a system composed of numerous lymphatic vessels which are directed towards the nodal sopradiaframmatiche and subdiaphragmatic. The lymphatic vessels are located generally in the space between the portal vein and hepatic artery and between the liver and bile ducts. They are classified into superficial and deep lymphatic vessels.
The superficial lymphatic vessels (located in the subserosal tissue amount) of the posterior, caudate lobe, the posterior portion of the lower face of the right lobe shall run with the inferior vena cava and pericavali draining lymph nodes, and lymph vessels of the ligament and coronary ligament Right triangular flow into the thoracic duct without passing through lymph nodes. The lymphatic vessels of the front face of the lower (except the rear portion of the right lobe) and the upper draining lymph nodes in the neurovascular bundle at the hepatic hilum. The lymphatic vessels of the lower surface and the posterior portion of the left lobe paracardiac draining lymph nodes, those of the right face and right side of the upper face draining celiac lymph nodes, following the course phrenic artery.
The deep lymphatic vessels, located in the liver parenchyma, represent a complex system of small blood vessels that lead to other size increasing, until the last few in number, tend to follow the course of the three hepatic veins, and then the inferior vena cava, draining pericavali lymph nodes. Those vessels located in the lower portion of the liver, draining vessels in size but more is in the lower door and draining lymph nodes at the hepatic hilum.
InnervationThe liver parenchyma is innervated by branches of the hepatic nerve plexus, consisting of the sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers, which enter through the hilum. Their course to accompany the ramifications of the bile ducts and hepatic artery, which provide vasomotor nerve fibers, while the hepatocytes are innervated directly. The ramifications of the parasympathetic nerve that descend along the bottom duct common bile duct, forming a plexus around the gallbladder, are mainly excitatory. Glisson's capsule is innervated by thin upper branches of the intercostal nerves.